The manner in which we consume media is undergoing a major shift and the traditional ways of accessing content, tied to terrestrial broadcasts or physical media, have been complemented (and often supplanted) by new-generation solutions. We are moving from long to short content, from HD to UHD, from static to adaptive stream, and so on. Similarly, terms like Over-the-Top (OTT) and Video-on-Demand (VOD) which are used interchangeably for video streaming have distinct workflows, technologies, and delivery mechanisms. Let us discuss these VOD OTT differences one by one.
VOD OTT Difference
OTT or over-the-top is partly a subset of VOD. If you consider a Venn diagram to understand the difference, then it overlaps with VOD when the streaming is limited to internet-based. But when it comes to live streaming, it is not VOD and is only covered under OTT.
Now, What is VOD?
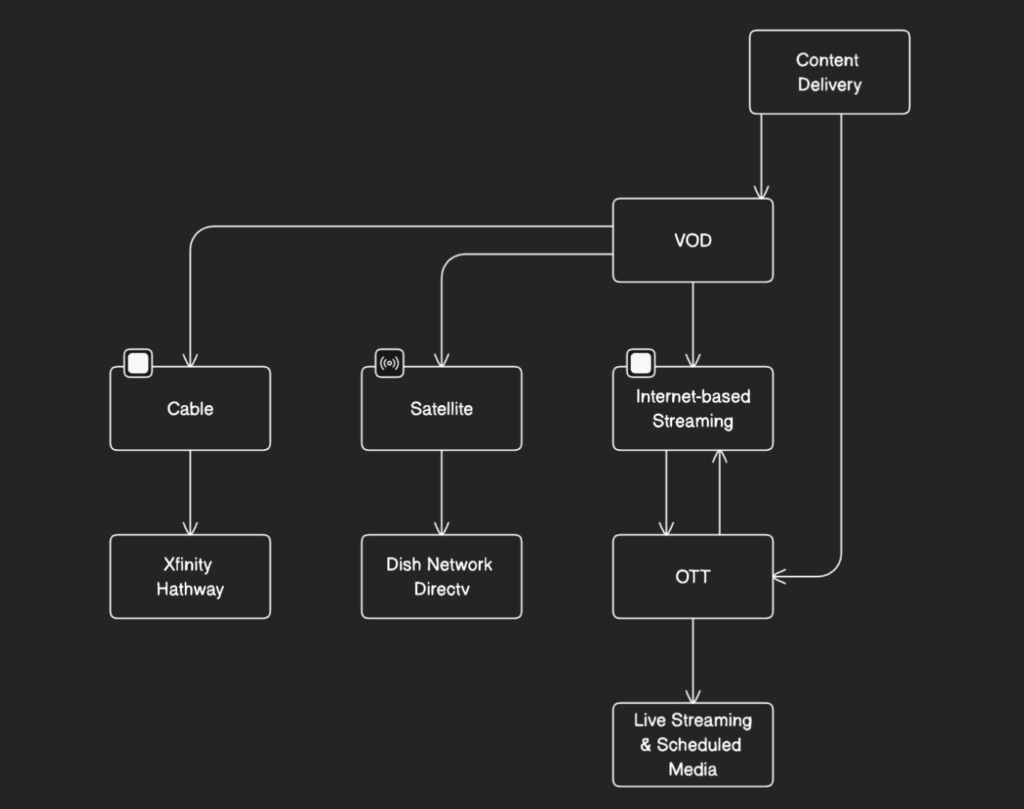
Video-on-demand or VOD is a video delivery mechanism that delivers video content, such as educational videos, movies, and TV shows, directly to customers for immediate viewing. VOD can stream through Cable, satellite, or Internet. Only the internet part comes under OTT, this means Netflix is a VOD as well as an OTT. Cable-operated VOD examples include Xfinity, Hathway, etc. and Satellite based VOD examples include Dish Network, Directv, Verizon Fios, Comcast, Cox, Time Warner Cable, Charter Spectrum, Broadstripe, etc. Also, pre-recorded videos distributed over private network settings for training, communication, and customer services, also come under the VOD head.
VdoCipher helps several VOD and OTT Platforms to host their videos securely, helping them to stop losing their video revenues.
OTT on the other hand transmits data over the internet. It doesn’t require users to subscribe to a traditional cable or satellite pay-TV service but you may need to subscribe to the internet service and also for paid content. OTT also includes live streaming and scheduled media programs getting distributed over the internet.
Remember, If the content is via satellite or cable and you cannot watch it whenever you want, it is neither a VOD nor OTT.
VOD Workflow Fundamentals
A Comprehensive VOD Workflow includes:
Content Acquisition:
- Source video content from creators or licensed sources.
- Ensure content is in a format suitable for processing and distribution.
Storage:
- Use robust storage solutions, considering redundancy and backup for safety.
- For internet-based streaming, cloud solutions like S3 buckets can be considered. For cable and satellite, dedicated data centers or storage facilities are used.
Content Transcoding:
- Convert source video into multiple formats and resolutions to cater to different devices and bandwidths.
- Use dedicated transcoding solutions. For internet-based platforms, services like AWS Elemental MediaConvert can be considered.
Content Delivery:
- Internet Streaming: Utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDN) to ensure fast and reliable content delivery to end-users.
- Cable and Satellite Streaming: Use dedicated broadcast equipment to send signals to set-top boxes or satellite dishes of subscribers.
Playback and User Experience:
- Provide adaptive streaming to ensure optimal video quality based on user bandwidth.
- Offer features like pause, rewind, and fast forward for enhanced user control. Also features like multi-language subtitles, chapters, player color, etc must be used wisely to enhance user experience.
- For cable and satellite streaming, consider using proprietary hardware-based players customized for your brand.
User Access and Management:
- Implement authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only subscribed users can access the content.
- Consider solutions like Amazon Cognito for internet-based platforms. For cable and satellite, proprietary access control systems are used.
Metadata Management:
- Store video metadata in robust databases. For internet-based solutions, databases like AWS DynamoDB can be considered.
- Metadata enhances searchability and user experience.
Security:
- Ensure DRM encrypted transmission of content which encrypts the content and also handles the key exchange securely.
- Implement secure access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
- Cable and satellite-based VOD providers need to integrate DRM with the hardware through proprietary ICs and processing hardware.
OTT Workflow Fundamentals
A Comprehensive OTT Workflow includes:
Content Acquisition:
- Source original content or acquire licenses for third-party content.
- Ensure content adheres to regional regulations and licensing agreements.
Storage:
- Store content in scalable and secure storage solutions.
- Cloud storage solutions, such as S3 buckets, are commonly used due to their scalability and global reach.
Transcoding and Packaging:
- Convert content into multiple formats suitable for various devices.
- Package content for adaptive bitrate streaming to ensure optimal quality based on user bandwidth.
- Consider using technologies such as CMAF for multi-format usage.
Content Protection:
- Implement Digital Rights Management (DRM) solutions to prevent unauthorized access and piracy.
- Different devices might require different DRM solutions.
Content Delivery:
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDN) to distribute content globally, ensuring low latency and high availability.
User Access and Authentication:
Implement robust user registration and authentication systems.
Analytics and Personalization:
- Video analytics can be used to analyze the user experience as well as to protect your content against unauthorized usage and password sharing.
- Offer personalized content recommendations based on user behavior and preferences.
- Monitor user behavior, content popularity, and streaming quality.
- Use analytics to drive business decisions.
Monetization:
- Implement chosen monetization models, whether subscription-based, advertisement-driven, or pay-per-view which are also called SVOD, TVOD, and AVOD.
- Ensure seamless payment gateways for subscription and pay-per-view models.
| Step | Internet-based Streaming / OTT | Cable and Satellite Streaming |
| Content Acquisition | Source from creators or licensed platforms | Source from creators or licensed platforms |
| Storage | Cloud storage (e.g., S3 buckets) | Data centers or storage facilities |
| Transcoding | Multiple format creation | Dedicated transcoding equipment |
| Delivery | CDN (e.g., Amazon CloudFront) | Broadcast equipment |
| User Access | Cloud-based access management | Proprietary access control systems |
| Metadata Management | AWS DynamoDB | Dedicated metadata databases |
| Security | DRM Encryption, secure access controls | Encrypted signals, secure access controls |
| Playback & User Experience | Adaptive streaming, interactive controls | Set-top box controls |
| Monetization | Subscription, pay-per-view, ad-based | Similarly, SVOD, TVOD, AVOD |
OTT Video Technology
In the realm of OTT, software-defined media supply chains have emerged as the linchpin, reshaping the broadcasting landscape. Here’s a deep dive into the technology underpinning OTT:
Software-Centric Infrastructure:
Legacy systems, being hardware-based, are infrastructure-centric and rigid. In contrast, OTT thrives on scalable, adaptable, web-centric platforms, achievable solely through software-based systems.
Packetization and Transport:
- OTT operates on the principle of packetization, segmenting data streams into manageable “chunks” for transport via HTTP.
- To counter challenges like latency and packet loss, OTT employs HTTP over TCP/IP.
- This protocol, with its acknowledgment mechanism, ensures packet delivery, retransmitting lost packets as necessary.
Content Delivery Mechanism:
- Traditional broadcasting pushes content, whereas OTT adopts a pull model. End devices request content, and OTT players retrieve and stitch together media chunks, creating a seamless stream.
- This pull model is facilitated by ubiquitous web browser protocols, with the receiver (or end device) controlling the transmission process.
- After Flash players became obsolete, HTML5 players can now handle smooth and secure delivery of video content with all advanced features.
Adaptability and Monetization:
- OTT platforms can host multiple content versions simultaneously. The player determines the optimal version, dynamically switching based on network performance.
- Monetization models include AVOD, SVOD, TVOD, and FAST. Personalized ad content can be interwoven with program chunks, thanks to the file-based nature of OTT.
Standards and Protocols:
- OTT leverages existing standards like MPEG2-TS for media carriage, various video compression schemes (e.g., MPEG-2, MPEG-4, HEVC), and audio formats (e.g., AAC, MP3).
- Unlike the rigid ISO broadcasting standards, the internet operates on RFC documents, with HTTP being foundational.
VOD Technology
Video-on-demand (VOD) technology has revolutionized the way audiences access content, offering flexibility across various platforms, including the Internet, cable, and satellite. It deploys the following technologies,
Multi-Platform Accessibility:
VOD isn’t exclusive to the internet. While web-based VOD platforms are prevalent, cable and satellite providers also offer extensive VOD libraries, allowing subscribers to select and watch content as they wish.
Content Storage and Retrieval:
Central to VOD is the content storage mechanism. High-capacity servers store vast content libraries, ready for retrieval upon user request. Efficient indexing ensures rapid content access and playback.
Streaming Protocols:
- For internet VOD, protocols like HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) are employed. These adapt video quality in real-time based on network conditions.
- Cable and satellite VOD utilize different protocols, often proprietary to the service provider, ensuring smooth content delivery over their specific infrastructure.
User Interface and Navigation:
VOD platforms, regardless of delivery method, prioritize user experience. Intuitive interfaces, search functionalities, and content categorization facilitate easy content discovery and selection.
Monetization and Content Models:
- VOD services can be free, subscription-based (SVOD), advertising-supported (AVOD), or transactional (TVOD), where users pay for individual content pieces.
- Integration of targeted advertising is also prevalent, especially in AVOD models, enhancing revenue streams.
VOD OTT DRM
Given the on-demand nature of VODs and OTTs, content protection is paramount. Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems are employed through DRM solution providers like VdoCipher which partners with Apple and Google for using their DRM license.
Explore More ✅
Vdocipher helps over 2500+ customers over 120+ countries to host their videos securely, helping them to boost their video revenues.
DRM offers a systematic approach to copyrighted protection of media content, ensuring secure distribution, and playback of digital video assets. It goes beyond mere encryption by managing the encryption key and enforcing specific content consumption rules set by content owners. This comprehensive system restricts unauthorized access, ensuring that premium content remains exclusive to paying subscribers.
For an end-to-end DRM solution, two core processes are pivotal: content packaging and content consumption. In content packaging, once media is created, it’s encoded and encrypted using a key from the DRM. This encrypted content is then transferred to storage or a content delivery network (CDN). During content consumption, the user’s device requests the content, which is delivered encrypted from the CDN. The device then initiates a license request from the DRM system, which processes this request and sends back a license containing the decryption key and associated rights. Also, key exchange is protected by hardware-backed black boxes for storing the private key.
Prominent players in the DRM space include Widevine (utilized by Google Chrome, Firefox, and Android platforms), and FairPlay developed by Apple for its ecosystems like iOS devices, Apple TV, QuickTime, and Apple Music. These systems ensure compatibility across a myriad of devices, from browsers to smart TVs.
With the adoption of content protection technology like DRM, unification efforts have also increased which is making the system more protected. Earlier, screen capture protection used to be limited to Apple Fairplay DRM but is now available on many of Google’s devices and software.
Advantages of OTT Platform over traditional VOD
OTT platforms deliver content over the internet, making it accessible from any device with an internet connection, anywhere in the world. VOD, especially when tied to cable or satellite, has high infra and distribution costs are also restricted to specific geographic regions or devices. Similarly, to remain updated traditional VOD systems might require significant hardware upgrades. Let us look at the advantages of OTT over traditional VOD through the following criteria.
| Criteria | OTT Platform | VOD |
| Accessibility | Accessible anywhere with an internet connection | Might be restricted to certain regions or devices |
| Infrastructure Cost | Generally lower due to the software-centric nature | Can be higher, especially for cable/satellite-based VOD |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and scalability | Might require hardware upgrades for scalability |
| Personalization | Advanced personalization based on user data | Limited personalization options |
| Monetization Models | Multiple models: SVOD, AVOD, pay-per-view | It might be limited to subscription or pay-per-view |
| Reach | Global reach | Often geographically limited |
| Content Update | Rapid updates with the latest content | There might be delays in content updates |
VdoCipher – Best VOD & OTT Video Solution Provider
We have learned in this article that VOD and OTT need to deploy many technical things to attain a complete workflow for their platform. The technology not only requires implementation but also expertise so that the whole system works in sync and does not become a bug-ridden structure. If we again want to list down, then these are the must-have features a VOD or OTT platform needs to have.
- Upload setup from desktop, Dropbox, Drive, Server, AWS, URL, FTP, and APIs to automate the upload process.
- High uptime cloud storage and processors
- Transcoding
- CDN
- Adaptive bitrates
- Custom video player
- DRM for video protection
- Dynamic watermarking to deter screen capture
- Video Analytics
- Plugins
- SDKs
- APIs
- Device compatibility for Desktop, Android, IOS, and IOS Native apps.
- Not limited to the above but also includes CMAF, Security analytics, easy integration, and much more.
All of the above are features that come with VdoCipher secure video hosting services. With good support and pocket-friendly pricing, it becomes a one and only choice as a video solution partner.
FAQs
What is an OTT Player?
An OTT (Over The Top) Player refers to the software application or embedded module that facilitates the playback of streaming audio, video, and other media content on OTT platforms via a web or app interface.
How do you get a custom player for your VOD & OTT platform?
VdoCipher provides a secure and customizable video player for OTT and VOD platforms. Once you’ve customized the player, you can easily embed it on your website or platform using the embed code for the web and app. The player is responsive and will adapt to various screen sizes, ensuring a seamless viewing experience for your audience. You can also integrate analytics to track viewer behavior and gather insights.
Supercharge Your Business with Videos
At VdoCipher we maintain the strongest content protection for videos. We also deliver the best viewer experience with brand friendly customisations. We'd love to hear from you, and help boost your video streaming business.


My expertise focuses on DRM encryption, CDN technologies, and streamlining marketing campaigns to drive engagement and growth. At VdoCipher, I’ve significantly enhanced digital experiences and contributed to in-depth technical discussions in the eLearning, Media, and Security sectors, showcasing a commitment to innovation and excellence in the digital landscape.